a) Department of Chemistry, The University, Sheffield, S3 7HF, UK.
b) BP Chemicals Ltd, Hull Research and Technology Centre, Saltend, Hull, HU12 8DS, UK.
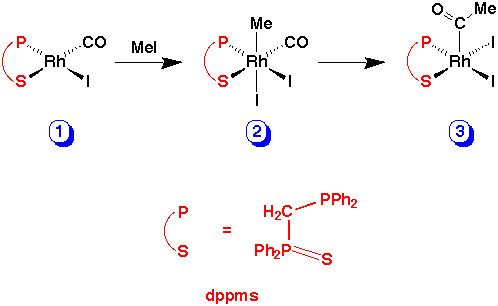
The chelating P-S ligand, Ph2PCH2P(S)Ph2 (dppms), has recently been shown to be unusually active in promoting the rhodium/iodide catalysed carbonylation of methanol to acetic acid.1 In this paper we present kinetic data concerning a key reaction in the catalytic cycle, the oxidative addition of methyl iodide to [RhI(CO)(dppms)] (1). The reaction leads to a stable acetyl complex, [RhI2(COMe)(dppms)] (3) via a methyl intermediate, [RhI2Me(CO)(dppms)] (2). We present evidence that both oxidative addition and migratory insertion steps are accelerated relative to the conventional Monsanto catalyst, [RhI2(CO)2]-, explaining the enhanced catalytic activity. We also report an X-ray crystal structure of the acetyl product, 3.
